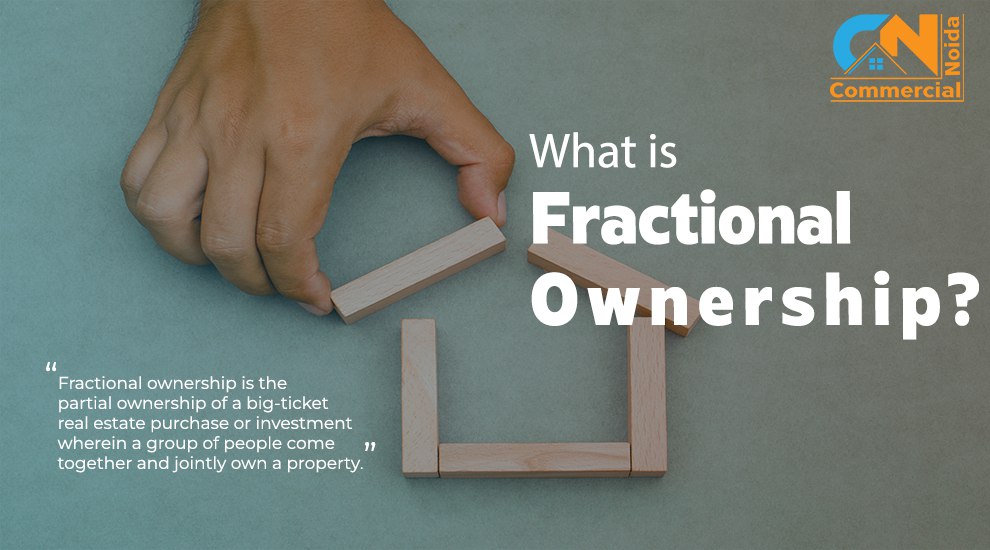
Understanding Repo Rate In Real Estate
If you have ever taken a loan from a financial institution, you know that we have to pay interest annually on the money we borrowed. Interest rates vary from bank to bank, and it significantly impacts the overall payable amount.
But have you ever wondered:
• How is the repo rate determined?
• And who regulates all this financial lending?
These are all regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). RBI sets its repo rate, which has a direct impact on the interest payable on the principal amount and the total payable overall.
The repo rate impacts every commodity that we purchase on loan, whether it is a car, bike, property, or anything else. But the question is:
• What is the repo rate?
• And how does it impact interest rates?
What Is Repo Rate?
The repo rate is also a kind of interest rate imposed by the RBI on banks for money borrowed. You might have been confused, so let's understand this with a simple example.
Suppose you have a bank and you don’t have any money. Now, if you don’t have money, you cannot provide loans and other transaction facilities to people for which you charge interest. As we know, a bank's source of income is interest and other charges applied on various transactions.
Now, if you don’t have money, it means no income from interest and other transactions. So, in times of cash crunch, banks take loans from RBI for which RBI has set a standard interest rate (Repo Rate). By borrowing money from the RBI, banks can carry on with their transactions in the time of cash crunch.
Is Repo Rate Good or Bad?
The repo rate plays a key role in influencing a country's economy by controlling the flow of money.
What Happens When Repo Rate Increases?
When the central bank (like the Reserve Bank of India) raises the repo rate, it makes borrowing money more expensive for commercial banks. As a result, banks tend to pass on this higher cost to customers, increasing the interest rates on loans like home loans, car loans, and EMIs. This helps control inflation by reducing borrowing and spending in the economy.
What Happens When Repo Rate Decreases?
On the other hand, when the repo rate is lowered, it becomes cheaper for commercial banks to borrow money. This encourages banks to lend more to businesses and individuals, leading to increased spending and investment.
In this way, the repo rate helps manage inflation and promote economic growth. By adjusting the repo rate, the central bank can either cool down an overheated economy or stimulate a sluggish one.
How Does Repo Rate Impact Real Estate ?
Repo Rate Impact On Real Estate
The repo rate, set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), plays a crucial role in the real estate market by influencing home loan interest rates. When the RBI increases the repo rate, borrowing costs for banks rise, leading to higher home loan interest rates. This makes loans more expensive, discouraging potential homebuyers, especially first-time buyers.
As a result, demand for residential properties tends to decrease. Conversely, when the RBI reduces the repo rate, home loan rates usually go down, making loans cheaper. This boosts demand for real estate, encouraging both residential and commercial property investments.
Impact On Property Rates
Interest rates are a key factor in determining property prices. A high repo rate can reduce the number of people able to afford home loans, causing developers to offer discounts or reduce property prices. On the other hand, a lower repo rate increases demand for properties, potentially raising prices in competitive markets.
Impact on Real Estate Developers
For developers, higher repo rates mean higher borrowing costs for construction projects, which can delay project completion or force them to raise prices. When repo rates are lower, developers can borrow more easily and often expand projects, potentially lowering prices and increasing the availability of affordable housing.
Impacts Market Sentiments
The repo rate also reflects broader economic conditions. A stable repo rate allows developers and investors to plan long-term projects with confidence, supporting economic growth and real estate market stability. Managing inflation and maintaining affordable borrowing encourages healthy market growth.
What is the Repo Rate for the Past 5 Years?
2024
• 8th August 2024: 6.50%
• 7th June 2024: 6.50%
• 8th February 2024: 6.50%
2023
• 8th December 2023: 6.50%
• 8th June 2023: 6.50%
• 8th February 2023: 6.50%
2022
• 7th December 2022: 6.25%
• 30th September 2022: 5.90%
• 5th August 2022: 5.40%
• 8th June 2022: 4.90%
• May 2022: 4.40%
2020
• 9th October 2020: 4.00%
• 6th August 2020: 4.00%
• 22nd May 2020: 4.00%
• 27th March 2020: 4.00%
• 6th February 2020: 5.00%
Conclusion
The repo rate is levied by the Reserve Bank of India on commercial banks (public and private) when they take loans in times of cash crunch. The increased repo rate increases the interest rate, while a decreased rate lowers the interest rate. It can impact real estate significantly, and the overall cost will be higher if the repo rate is high and lower if it is low.














































































































.webp)

































































































.webp)
















































































.webp)