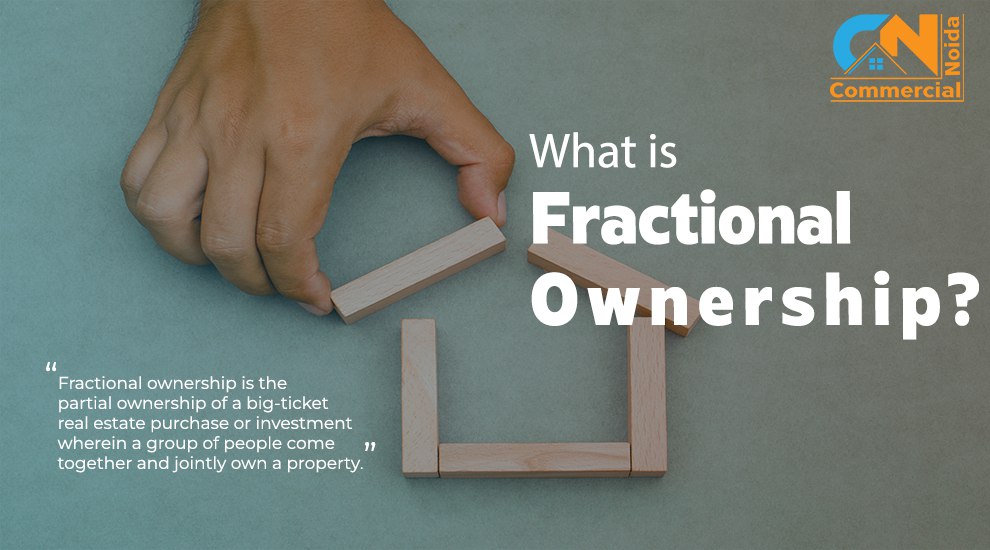
Understanding Taxation on Rental Income in India
Real estate is often considered a lucrative investment avenue in India due to its potential for generating passive income. Rental income from properties offers financial security and helps individuals build a notable fund for retirement. However, it is crucial to understand the taxation rules governing rental income to maximize earnings and simultaneously save on taxes. Let’s delve into the essential aspects of rental income taxation in India.
Income from House Property: Tax on Rental Income
Before diving into the taxation of rental income, it’s essential to understand the various sources of income categorized under the Income Tax Act (ITA). The five heads of income include:
• Income from salary
• Income from business profits or gains from profession
• Income from house property
• Income from capital gains
• Income from other sources
Real estate investments can be broadly categorized into residential and commercial properties. While residential investments offer a regular flow of rental income and steady capital appreciation, the commercial real estate sector has become increasingly profitable due to expanding economic opportunities.
Different Types of Rental Income
Rental income can stem from various sources, each with its tax implications:
1. Income from House Property: This encompasses rental income from buildings, apartments, or land, including advance payments like security deposits.
2. Rental Income from Partly Self-Occupied House Property: When an owner partially occupies the property and rents out the rest, separate taxation rules apply for each portion.
3. Rental Income from Composite Rent: In cases where a property is leased along with its assets, like furniture or appliances, distinct tax treatments are applied to the property and other assets.
4. Rental Income from a Shop: Income earned from letting out a shop situated on owned land falls under income from house property.
Tax on Rental Income in India
Rental income is primarily taxed as ‘income from house property’ in India. Property owners receiving rent for residential or commercial properties are liable to pay taxes on this income. The tax calculation is based on the property’s Gross Annual Value (GAV) after deducting municipal taxes, home loan EMIs, and standard deductions.
How to Calculate Tax on Rental Income?
Calculating tax on rental income involves several steps:
1. Calculate Expected Rent: Estimated rental income based on municipal valuation.
2. Determine Gross Annual Value (GAV): Choose the higher expected or actual rent.
3. Calculate Net Annual Value (NAV): Deduct municipal taxes from GAV.
4. Apply Standard Deduction: Up to 30% deduction on NAV for repairs and renovations.
5. Claim Deductions on Housing Loan Interest: Deduct interest paid on home loan from taxable income.
6. Taxable Income: The remaining amount after deductions is the taxable rental income, taxed as per the individual’s tax slab rate.
How to Save Taxes on Rental Income?
Several exemptions and deductions can help reduce tax liability on rental income:
1. Standard Deduction: Claim up to 30% deduction on NAV for repairs and maintenance.
2. Unpaid Rents: Adjust unpaid rents or emptiness against rental income.
3. Tax Benefits on Home Loans: Deduct interest paid on home loans up to ?2 lakh, and claim additional benefits under Section 80 EEA.
4. Tax Benefits for Property Co-Owners: Co-owners can claim deductions based on their ownership shares, reducing overall tax liability.
Conclusion
Understanding the taxation rules for rental income is crucial for property owners to optimize their earnings and minimize tax liabilities. Real estate remains a popular investment avenue in India, providing a reliable source of passive income, especially for retirees. By leveraging available exemptions and deductions, property owners can maximize their rental income while complying with tax regulations.























































































































.webp)

































































































.webp)















































































.webp)