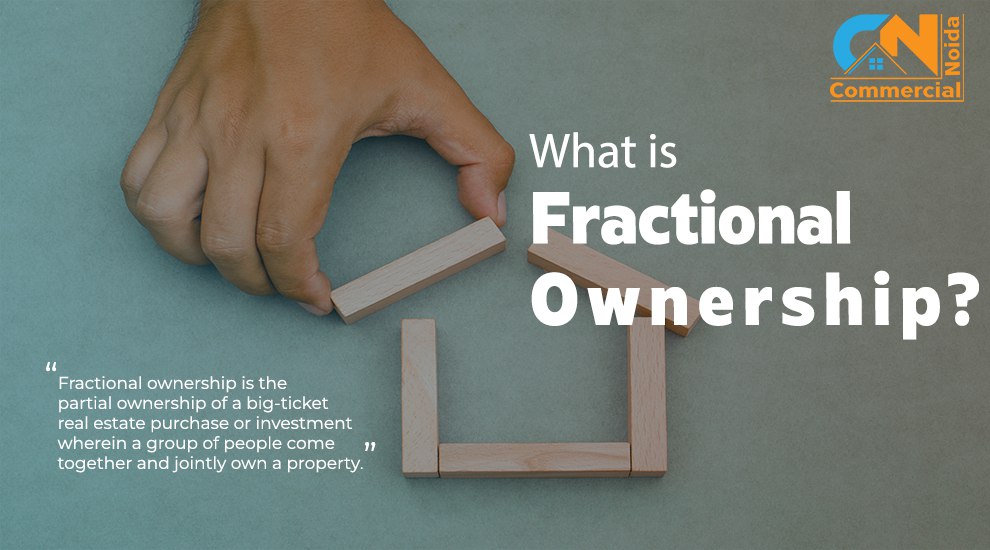
Real Estate Laws and Regulations in India
Before you decide to buy a property in India, it's essential to understand the laws that govern real estate transactions in the country. These laws are made by both the central and state governments, ensuring that buying or selling property is fair and legal for everyone involved.
What are Real Estate Laws?
Real estate laws in India cover everything related to land and buildings, whether residential (where people live) or commercial (where businesses operate). These laws are fundamental because they protect buyers and sellers during property transactions. The Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) is one such law that oversees how real estate projects are marketed, sold, and developed in India. This law makes sure that developers follow rules that protect buyers' interests.
Critical Real Estate Laws in India
Let's look at some of the important laws you should know about before buying property:
1. Registration Act, 1908 and India Stamp Act, 1899
These laws concern registering documents related to property transactions and paying stamp duty (a kind of tax). They ensure that all property transactions are officially recorded, which is important for legal proof of ownership.
2. Real Estate Regulation and Development Act (RERA), 2016
RERA was created to bring transparency and accountability into the real estate sector. All real estate projects must be registered with the authorities before they can be sold. This law helps protect buyers from unfair practices and ensures that projects are completed on time.
3. Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act, 2013
This law is essential when the government acquires land for public projects. It sets rules for compensating and rehabilitating people affected by such acquisitions. This ensures that people are treated fairly when their land is taken for public use.
4. Transfer of Property Act, 1882
This law deals with how property ownership can be transferred from one person to another. It covers different ways of transferring property, such as selling, giving it as a gift, or putting it up as security for a loan.
5. Indian Contract Act, 1872
This law applies to all contracts in India, including those related to property. It defines how contracts are made, what happens if they are broken, and what rights people have when they make property agreements.
6. Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999
FEMA deals with investments from people who do not live in India (Non-Resident Indians, or NRIs). It has rules about how NRIs can buy property in India and what they need to do to invest in real estate.
Can NRIs Buy Property in India?
If you are an NRI or a person of Indian origin living abroad, you can buy residential property in India. However, rules and restrictions are depending on your status. Non-Indian foreigners generally can only purchase property in India if it's inherited.
Conclusion
Understanding these real estate laws is crucial before you buy property in India. They protect your rights as a buyer and ensure that the transaction is legal and fair. Whether registering your property under the Registration Act, understanding the transparency guaranteed by RERA, or knowing your rights under the Transfer of Property Act, these laws provide a framework for smooth property transactions. For NRIs and foreign investors, compliance with FEMA guidelines is necessary to invest safely in Indian real estate.
Knowing these laws allows you to make informed decisions about buying property and avoid legal issues later. Always consult with legal or real estate professionals to ensure you understand how these laws apply to your situation. This knowledge will empower you to navigate the real estate market in India confidently and securely.


















































































































.webp)

































































































.webp)















































































.webp)