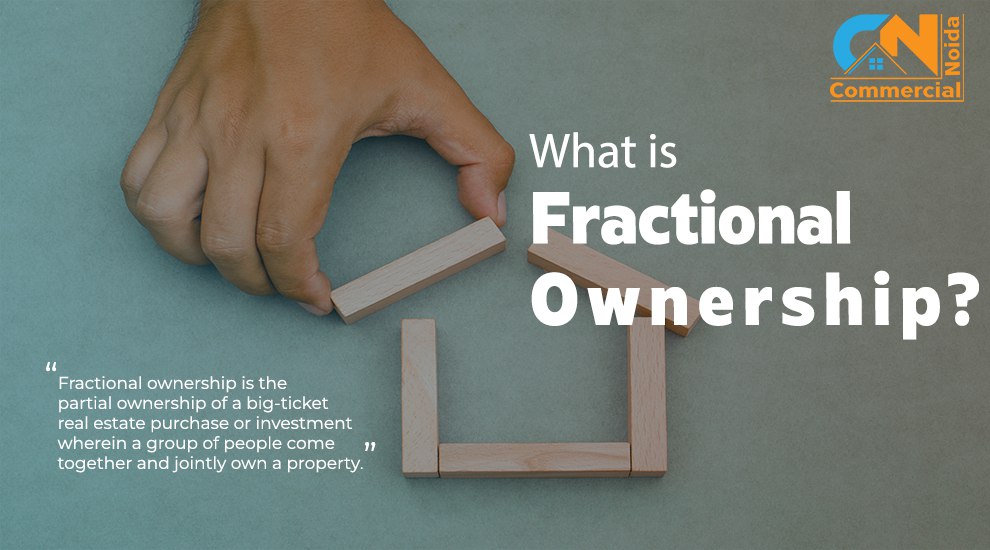
Types Of Interest Rates In India
Have you ever obtained a loan, or are you considering one? You've heard of interest rates. Every bank displays various interest rates, such as 8, 9, 10, or 12 percent per annum. Have you ever explored the various classifications of interest rates in India? If you are well-versed in these types, you can secure your loan at the most competitive rates, potentially saving a significant amount of money.
What are interest rates?
Interest rates are essentially the cost of borrowing money, typically expressed as a percentage of the principal loan amount. For instance, if a bank sets its interest rate for a personal loan at 12 percent annually.
You will be required to pay the bank 12 percent of 1 lac, which equates to 12k in interest plus the principal amount of 1 lac, for a total of 1 lac 12 thousand. If you decide to extend the loan for three years, your interest rate of 12k per annum will result in a total payment of 1 lac 36 thousand.
What are the 3 types of interest ?
In India, there are various types of interest rates, including fixed interest rates, floating interest rates, and compound interest rates, among others. Knowing the types of interest rates is important when making informed financial decisions.
Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed Interest Rate A fixed interest rate remains the same throughout the loan term, providing consistency in monthly payments. For example, if you take a loan with a fixed interest rate of 10%; you will pay 10% interest on the principal amount for the entire duration of the loan.
Let's say you take out a loan of 100,000 with a fixed interest rate of 5% per year for 3 years. The interest remains constant throughout the loan period.
• Principal Amount (P): 100,000
• Fixed Interest Rate (r): 5% per year
• Time Period (t): 3 years
Yearly Calculation
• Interest for Year 1: Calculation: 100,000 * 0.05 = 5,000
• Interest for Year 2: Calculation: 100,000 * 0.05 = 5,000
• Interest for Year 3: Calculation: 100,000 * 0.05 = 5,000
• Total Interest: Calculation: 5,000 * 3 = 15,000
Total Amount Payable
Calculation: 100,000 (Principal) + 15,000 (Interest) = 115,000
Floating Interest Rate
A floating interest rate fluctuates based on economic fluctuations. Therefore, the interest rate may fluctuate between 6 percent and 8 percent, depending on the prevailing economic conditions. It totally depends on RBI.
So suppose RBI lends money to a bank at a 4 percent repo rate, and the bank gives you a loan at 7 percent, which means 3 percent is the difference. Now assume the repo rate for the next quarter increased by RBI by 2 percent, meaning 6 percent; now your loan interest would be 9 percent. Therefore, you remain unaware of the bank's actual lending cost until the announcement of the repo rate.
Example:
You take out a loan of 100,000 with a floating interest rate that is initially set at 6%. The interest rate changes every year based on market conditions.
Yearly Calculations
Initial Year (Interest Rate: 6%):
• Principal Amount: 100,000
• Interest for Year 1: 6,000
• Total Amount at End of Year 1: 106,000
Year 2 (interest rate increases to 7%):
• New Principal Amount: 106,000
• Interest for Year 2: 7,420
• Total Amount at End of Year 2: 113,420
Year 3 (interest rate decreases to 5%):
• New Principal Amount: 113,420
• Interest for Year 3: 5,671
• Total Amount at End of Year 3: 119,091
Total Interest Paid Over 3 Years: 19,091
Total Amount Payable at the End of 3 Years: 119,091
This example shows how the interest amount changes each year based on the fluctuating interest rate, ultimately affecting the total amount payable.
Compound Interest Rates
Compound interest is a type of interest rate. Both the principal year and the interest amount accrue compound interest. For example, let's say you have taken a loan of 1 lac with 7 percent interest on it. If the loan has a 5-year tenure, your total repayment will be 1 lac, 40 thousand, and 255 rupees.
You might be wondering how this is possible. The annual interest rate is more than 12 percent, but my interest rate was only 7 percent. Let's understand this breakdown.
• First-year amount + interest = 1 lac + 7k
Beginning with the second year, we will no longer fix the interest rate at 1 lac; instead, we will calculate it based on the entire amount of 1 lac and 7k, which will become the new principal. So the second-year amount will be
• 1 lac 7k * 7% = 1 lac 14k and 90 rupees.
• In the third year, it's 1,14,090 × 7% = 1,22,504.30 rupees.
• In four years, it's 1,31,079.61 rupees.
• In the fifth year, 140,255.17 rupees
Therefore, the total payable amount comes to 1 lac (40k) and 255 rupees.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of interest rates equips you with valuable information when choosing a loan. It helps you decide what loan is best and how much to pay. Knowing these types and their rates will help you manage your finances more proficiently.














































































































.webp)

































































































.webp)
















































































.webp)