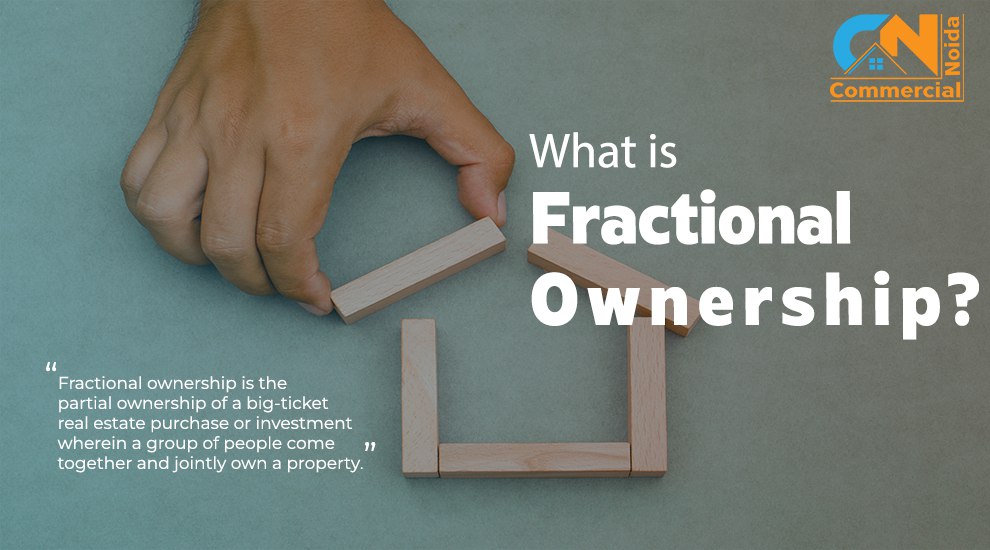
Top 12 RERA Guidelines Every Investor Must Follow
Indian real estate was unorganised and full of difficulties until the RERA Act came into force in 2016. Indian parliament made it mandatory for every state to establish a Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) to regulate real estate with the RERA act and rules of the respective state and protect the rights of buyers and investors.
But still, some buyers and investors get fooled by the developers. Today, we will educate you about the 11 rules of RERA and how they protect you from being cheated.
Rera Act And Rules
Every buyer should know these 11 RERA acts and rules of RERA to ensure the project is legal and validated by the governing authority. Knowing these rights will protect your rights and help you save yourself from being fooled.
#1 RERA Registration
RERA has made it mandatory for the developers to register the land on which the project will be constructed if the land area exceeds 500 square metres or more than 8 units. Builders are not allowed to sell or advertise the project before it gets RERA registered; otherwise, heavy penalties can be imposed, and the RERA can dispose the project.
#2 Agreement For Sale
Rera has set a standard format for agreement for sale documentation; every developer is bound to use it only. So, always refer to the standard format RERA sets for agreement for sale. Here is the link for the standard deal for sale format: Agreement for sale format pdf.
#3 Carpet Area
As per the rules specified by RERA, builders or developers must disclose the carpet area in the Brochure or Agreement for sale document. The carpet area is also called the net usable area in the building or where a carpet can be spreaded.
As per RERA, this is the definition of Carpet AREA!
Section 2(k) in Real Estate (Regulation And Development) Act, 2016
"carpet area" means the net usable floor area of an apartment, excluding the area covered by the external walls, areas under services shafts, exclusive balcony or verandah areas, and exclusive open terrace areas, but includes the area covered by the internal partition walls of the apartment.
Read More: How To Identify Risky Projects On Rera’s Website?
#4 Agent Registration
Real estate agents must register with RERA and need RERA registration to be authorised to work on any project. Developers must include the names of the agents associated with the project at the time of registration. If the developer still needs to remember to do so, they must update it with RERA soon; otherwise, no agent will be entitled to work on that specific project.
#5 RERA Escrow Account
RERA Escrow account–is a separate account that the developer or promoter maintains with RERA at a local bank authorised by RERA and the builder to keep money where the project is being constructed.
In this account, the builder is required to keep 70 percent of the total money collected, and the builder can use the remaining 30 percent for other purposes associated with the project.
Withdrawals from the RERA Escrow Account Must be Certified by the Project Engineer, Architect, and Chartered Accountant. These Accounts must be Audited each Financial Year, and a Copy must be submitted to the Authority.
#6 Early Payment
RERA says a developer can only take up to 10 percent of the unit's total cost from the buyers until he gets into a written agreement.
#7 Quarterly Progress Report
Builders should update their project details every three months. This means they need to share important information like how many units they've sold, what approvals they’ve received, and any certificates from experts. Buyers can easily track how the project is going online by doing this regularly.
#8 Lodging Complaint
If you have a problem with the builder, agent, or promoter, you can file a complaint with RERA (Real Estate Regulatory Authority). RERA will handle your complaint and try to resolve it within two months of receiving it.
#9 Changing Project Approved Plans
If the builder wants to change the project's approved plan, they need approval from at least two-thirds of the people who have bought units.
#10 What Is Section 16 Of The Rera Act?
Section 16 of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act of 2016 says that builders must get insurance for their real estate projects. This insurance has to cover things like the land and building title, the construction work, and any other types of insurance that the government might decide later.
However, this section won’t be in effect until the government tells us exactly how and when it will start. The main goal of this act is to protect people buying homes and to make investing in real estate more appealing.
#11 What is rule 24 of RERA?
When carrying out orders from RERA, like giving possession of homes to buyers and registering their units, the rules are set out in Section 40(2) of the RERA Act and Rule 24 of the U.P. RERA Rules.
Rule 24 says that RERA should carry out these orders like a court order. Out of 5586 requests for implementing these orders, RERA has completed about 3000 of them. This means roughly 54% of the requests have been handled.
#12 What is Section 37 of the RERA Act?
Section 37 of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) says that the authority in charge can give orders to promoters, buyers, or agents. These orders are meant to help them follow the rules of the Act or any related regulations. Once the authority gives these orders, everyone involved must follow them.
Conclusion
Understanding RERA rules helps protect buyers and investors in real estate. Key points include:
• Ensuring projects are registered.
• Knowing your rights regarding payments and progress.
• Having avenues to lodge complaints.
Familiarise yourself with these RERA act and rules to safeguard your interests and make informed real estate decisions.


















































































































.webp)
































































































.webp)
















































































.webp)